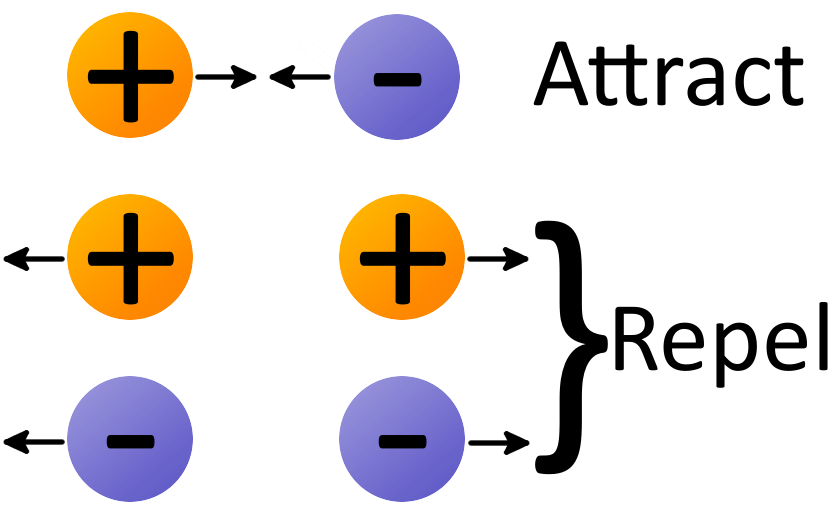
Electric Charge is that physical property of matter due to which the other matter experience a force when matters are placed in electromagnetic field. Electric charge is also known as Charge, Electrical Charge and Electrostatic Charge. It is denoted by symbol ‘q’. It is a scalar quantity as charge has only magnitude and no direction.The two types of charges exist in nature: Positive and Negative Charge.Same charge repels each other and opposite charge attract each other. In the figure given below, we can see that like charge are repelling each other, while opposites are attracting each other.We know that in a nucleus proton and neutron exists while electron revolve around the nucleus. Proton (p+) have positive charge and electron (e-) have negative charge. As symbol of proton is (p+) so proton carrying positive charge and symbol of electron is (e-) so electron carrying negative charge. As number of proton and electron in a nucleus are equal so net charge on nucleus is zero.For existing the net charge on a body the sum of positive and negative charge should be equal to zero.Properties of Electric Charge
Electric Field
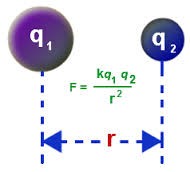
It is the region around a charge particle or object due to which another charge particle or object experience force. Electric Field is a vector quantity so we must consider the sign in numerical.Formula of Electric FieldUnit of electric field: E = N/CAs, unit of force is Newton (N) and charge is Coulomb ( C), So unit of electric field is N/C.Note: While writing the unit 1st letter should be capital.In the above formula F is the force and q is the charge. F is calculated in terms of coulombs law.Coulombs law is stated as force acting on a charge particle due to another charge particle is directly proportional to product of their charges and inversely proportional to square of distance between the charges.Where, k is the proportionality constant and its value is 9 * 109 Nm2/C2. It is different for different medium.SI unit of F is = N m2 C2/C2 m2So, on solving above equation we get F = Newton (N)How to calculate SI Unit of any Physical Quantity?
These four quantities are the basic quantities with the help of these quantities we can find the SI unit of any other physical quantity.We, know that formula of E is = F/qSo, SI unit of F is Newton and Charge is Coulomb.E = N/CHow to calculate the Direction of E?
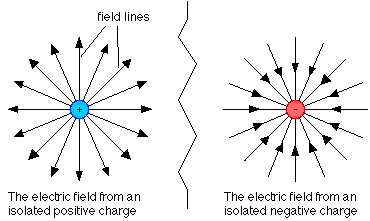
Direction of Electric Field is always from positive charge to negative charge. In terms of single positive charge Electric field move away from the positive charge as shown in the first part of the diagram and in terms of negative charge Electric field move towards the negative charge as shown in the second part of the diagram.In the above diagram, we can see that in terms of positive charge E is moving away from positive charge Similarly in terms of negative charge E moving away from negative charge.Diagram of E in terms of two Charges
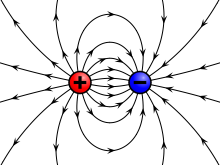
In this diagram, all the three directions are used. Firstly, Electric field goes from Positive charge to negative charge. Secondly, In terms of positive charge field lines are moving away from positive charge and in terms of negative charge field lines are coming towards the charge.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Two insulated charge sphere A and B of identical size having charges qA and -3qA respectively. When they are brought in contact with each other and then separated what are the new charges on them?Sol. As two charges are of opposite sign, they will attract each other so there will be the simple addition of charge.New charge on them is Q = (qA) + (-3qA / 2)Q = -qAQ2. What is the basic condition for existing the net charge on a body?Sol. The basic condition for existing the net charge on a body is that number of positive and negative charge should not be equal to zero.Q3. What is the Charge on Electron?Sol. Charge on electron is -1.6 *10-19 C.Q4. Is the force acting between two point charges q1 and q2 kept at some distance apart, attracting or repulsive (a) q1 q2 > 0 (b) ) q1 q2 < 0 ?Sol.(a) If q1 q2 > 0 then the force is repulsive because if both the charges are positive and negative (same charges) only then their product is greater than zero. We know that same charges always repel each other.(b) If q1 q2 < 0 then the force is attractive because one charge will be positive and other will be negative and opposite charge attract each other.Q5. What is the SI unit of Electric Field?Sol. SI unit of electric field is N/C.Q6. What is the Dimensional Formula of Electric Field?Sol. The dimensional formula of electric field is [MLT-2C-1].Q7. If two charges having equal magnitude are separated by unit distance and exert a force of 15 N on each other. What will be the force exerted by the same charges kept at same distance but the charges are placed in water?Sol.F1 = 15 N, r1 = 1 meter, k air = 1 , q1 = q2 = qF2 = 15 N, r2 = 1 meter, k water = 80F1 = k air q1 q2 / r2, F2 = k water q1 q2 / r2F2 = k water q1 q2 / r2F2 = 80 * q2/ 1F2 = 80 q2 N.Q8. Two spheres of radius r1 and r2 are connected by a wire. What will be the ratio of their electric field?Sol. We know that F= k q1 q2/r2 and E = F/q.So, E1/E2 = r22/r12.What is Electric Charge?
Electric Charge is a physical property of matter due to which a matter experience a force on another charge matter when placed in electromagnetic field (electric or magnetic field).Another Definition of Electric Charge
According to Franklin electric charge is used for electrostatic interaction. For Example: A body can interact with another body only if charge is present in that body.
What is the definition of charge in daily life?
In daily life we use the term charge many times. For Example: charging a phone. We can charge an object when we apply voltage to it.Q= CVQ = Charge, C = Capacitance, V= Voltage.How Charge Originate?
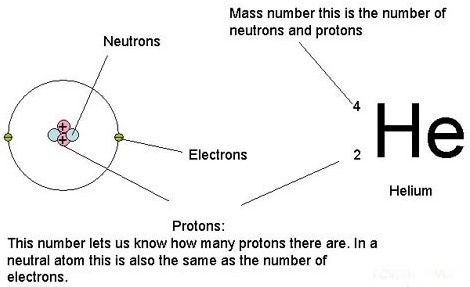
It was assumed that origin of charge start from atomic structure. Let us consider a atom having size 10 -10 meter. Inside the atom nucleus in present and size of nucleus is 10 -15 meter. Electrons revolve around the nucleus. As we know that symbol of proton is (P + ) so charge on proton is + and symbol of electron is (e – ) and charge on electron is – so from sign convention we can tell that the object is positively charged or negatively.In the above figure we can see that how charge originate from the atomic structure. From the atom electrons and protons originate.What is SI unit of Charge?
What is Elementary Charge?
Elementary Charge is the magnitude of charge carried by single electron or proton. The charge on electron is negative and it is denoted by (-e) while the charge on proton is positive and it is denoted by (+e).The charge on single proton is (+ 1.6 * 10 -19 C ) while the charge on single electron is (- 1.6 * 10 -19 C).How many types of charge exist in nature?
There are two types of charge exists in nature:
- Positive Charge
- Negative Charge
“Same charge repel each other and opposite charge attract each other”In the diagram given below we can see that same charge repel each other and opposite charge attract each other.Note : In case of neutral charge number of positive charge is equal to the number of negative charge but neutral charge is not considered the type of charge. There are only two types of charge exist. For Example: Positive and Negative.What are the Properties of Electric Charge?
How Electrons Come out from the Neutral Object?
Let us consider a neutral object (equal number of proton and electron). In neutral object each electron is attracted to each proton (because number of positive charge is equal to number of negative charge). The force we are applying to pull electrons from the object is equal to the force which is pulling back electrons to the charged object because amount of positive charge is equal to the negative charge, so both forces cancel out with each other. So we have to do some external work to pull the electrons from the object.There are various method to pull the electrons from the surface.
How can we charge an object?
How Electric Field can generate from Charge?
In case of positive charge direction of electric field is away from the charge while in case of negative charge direction of electric field is towards the charge as shown in the figure.What is Current?
Current may be defined as charge flowing through a closed circuit per unit time.Another Definition of Electric Current
A current is said to be one Ampere if charge of one Coulomb flows through a point in one Second.I = q/tIn above figure, current is flow in the circuit when we apply the voltage to the circuit the charge generates and electrons flows in the circuit. The direction of current is opposite to the direction of flow of electrons.What is Formula of Current?
I = q/tWhere, I is the current flowing in the circuitt is the time.What is SI Unit of Current?
SI unit of current is Ampere.What is Dimensional Formula of Current?
Dimensional formula of current is [ CS-1 ].Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the definition of charge?Sol. A charge is said to be one coulomb if one Ampere current flows in a circuit in one second.Q2. What are positive and negative charge?Sol. A neutral atom becomes an ion if it loose or gain electron or proton. As we know that neutral atom don’t have any charge it becomes positive charge if it loose electron and it becomes negative charge if it gain electron.Q3. What is the unit for measurement of charge?Sol. The unit for measurement of charge is coulomb.Q4. What is an electric current?Sol. Electric current is the ratio of charge per unit time.Q5. Why do two electrons repel each other?Sol. Two electrons repel each other because both the electrons have same charge. For Example: Negative and we know that same charge repel each other.
We are Leading Institute providing Regular / Vedioes / Live Coaching under NVIE Trust . We Provides Coaching For Classes 1 to 12 (CBSE - CHSE - ICSE - HSC ). We also provide NEET - JEE -OUAT Entrance Preparation for +2 Science Student . We provide Bank - Railway - SSC - OTET - OSSTET - B.Ed Odisha - CT Odisha - Others Entrance Coaching for graduate .
Join Us ! Join Us ! Join Us !
- November 04, 2019
Physics
Electrostatic Potential
Capacitance
Current Electricity
Moving Charges & Magnetism
Magnetism & Matter
Electromagnetic Induction
Alternating Current
Electromagnetic Waves
Ray Optics & Optical Instruments
Wave Optics
Dual Nature Radiation & Matter
Atoms
Nuclei
Semiconductor Electronics
Communication Systems
Electric Circuits
Potentiometer
We are Leading Institute providing Regular / Vedioes / Live Coaching under NVIE Trust . We Provides Coaching For Classes 1 to 12 (CBSE - CHSE - ICSE - HSC ). We also provide NEET - JEE -OUAT Entrance Preparation for +2 Science Student . We provide Bank - Railway - SSC - OTET - OSSTET - B.Ed Odisha - CT Odisha - Others Entrance Coaching for graduate .
Join Us ! Join Us ! Join Us !
- November 04, 2019
Course-I
PHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATION
Unit-1: Introduction to Philosophy and Education
1.1 Concept and Scope of Philosophy
1.2 Concept and Scope of Education
1.3 Types and Functions of Education
1.4 Relationship between Philosophy and Education.
1.5 Philosophy and aims of Education
Unit-2: Indian Education: Historical Perspective
2.1 Education during Ancient Period (Vedic Education, Buddhist Education and Jains)
2.2 Education during Medieval Period (Including Islamic Education)
2.3 Education during Modern Period (Pre-Independent and Post Independent era)-1
2.4 Education during Modern Period (Pre-Independent and Post Independent era)-2
2.5 Education During Modern Period-3 i. Rabindranath Tagore ii.Sri Aurobindo Gosh iii. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi iv. Jiddu Krishna Murthy v. Dr.BR.Ambeddkar vi Moulana Abdul Kalam Azad
Unit-3: Eastern Systems and Western Schools of Philosophy
3.1 Eastern Systems of Philosophy i. Sankhya ii. Yoga iii. Nyaya iv. Vedanta
3.2 Western Schools of Philosophy i. Idealism ii. Naturalism iii. Pragmatism iv. Existentialism
Unit-4: Value Education
4.1 Concept of Value
4.2 Classification of Values
4.3 Value Crisis
4.4 Approaches to inculcate Values
4.5 Values and Harmonious Life
Unit-5: Teaching as a Profession
5.1 Teacher: Professional Competencies and Commitments
5.2 Teacher as a Nation Builder
5.3 Teacher as a Creator and Facilitator of Knowledge
5.4 Professional ethics of teachers
5.5 Important Question
Course-II
PERSPECTIVES IN CHILD DEVELOPMENT
1.1 Concept of Growth, Development and Maturation
1.2 Principles of Development
1.3 Stages of Growth and Development (Infancy Childhood, Adolescence)
1.4 Dimensions of Growth and Development (Physical, Cognitive, Emotional,Social,Moral, language)
1.5 Longitudinal and cross sectional approaches of understanding development
1.6 Important Question
Unit-2: Theories of Development
2.1 Cognitive theory of Development (Piagetıs)
2.2 Psycho-social theory of development (Erikson).
2.3 Theory of Moral Development (Kohlbergıs).
2.4 Theory of psycho- sexual development (Freud).
2.5 Theory of Emotional Development (Goleman).
2.6 Important Question
Unit-3: Childhood as a period of Socialization
3.1 Characteristics of childhood – developmental tasks.
3.2 Child development – Physical, cognitive, social, emotional, moral and language Development during childhood.
3.3 Child in different socio-cultural contexts.
3.4 Process of socialization – conflicts resolution and social development.
3.5 Stages of Social development – Isolated play, parallel play and social play. Characteristics of socially matured person.
3.6 Important Question
Unit-4: Adolescence as a period of transition
4.1 Characteristics and needs in Adolescence
4.2 Genesis of problems during adolescence-Physical, cognitive, emotional, social, Moral and language development
4.3 Adolescent Groups – Gangs
4.4 Mechanisms of adjustment with special reference to defense mechanisms and Holistic development
4.5 Leadership: Types of Leadership, Development of Leadership qualities in Adolescents and its educational implications.
Unit-5: Individual Differences
5.1 Dimensions of Individual differences-cognitive abilities, interests, aptitude, Creativity, personality and values
5.2 Theory of multiple intelligence (Gardner) – Implications for understanding Differences in children
5.3 Difference in children based on learning styles and socio cultural context (home Language and Instructional language)
5.4 Individual differences based on cognitive abilities – learning difficulties, slow Learners and intellectually challenged, intellectual giftedness - implications for Catering to individual variations in view of “differences” rather than “deficits” Perspective.
5.5 Fostering creativity among children.
Course-III
INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT) FOR ENRICHING TEACHING AND LEARNING
1.1 Educational Technology – Concept, Growth, Objectives, Characteristics, Advantages, Challenges and Impact
1.2 Information Technology - Knowledge Explosion, Preservation and Retrieval
1.3 Communication – Concept, Elements, Process, Barriers & Types – Teaching as Communication - Communication Technology – Its application in Education
1.4 Instructional Media and Aids – Aural, Print, Visual and multimedia
1.5 Concept, Importance, Characteristics and Scope of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Unit-2: ICT in Education
2.1 Knowledge Acquisition and Multi-sensory approach
2.2 Classroom Communication and Communicative Skills for Teachers and Students - Flanderıs Interaction Analysis Category System
2.3 Individualised Instruction – Concept, Need, Principles and Techniques
2.4 Programmed Learning - Principles, Types, modes of presentation, development, Application and role of teacher
2.5 Changing roles of the learner and the teacher in ICT-Integration and Challenges
Unit-3: Computer Fundamentals and Applications
3.1 Types, Characteristics and features of Computers
3.2 Components of Computers – Hardware, Software, Memory and Maintenance of Computers
3.3 Operating Systems - DOS, Windows and Macintosh and Mobile Apps for Teaching
3.4 Software for Word Processing, Presentation, Statistical & Graphical, Page Layout, multimedia and webpage creator
3.5 Concept, Applications and Challenges of Computer networks, Internet, E-mail and Digital Space
Unit-4: ICT Enriched Learning Experiences
4.1 Application of ICT for Enriching Classroom Experiences
4.2 Application and use of Multimedia Educational Software for classroom Situations
4.3 Use of Internet based media for teaching and learning enrichment - Acknowledgement
4.4 Project based learning using computers, Internet and Activities
4.5 Collaborative learning using group discussion, projects, field visits, blogs, etc.
Unit-5: Application of Computers in Education
5.1 Computer as a learning tool – Concept of E-learning
5.2 Web 2.0 Technologies-characteristics, types and examples
5.3 Virtual Classroom, Smart Boards, Tools and Opportunities
5.4 Open Educational Resources – Concept and Significance
5.5 Critical issues in Internet usage – Authenticity, Addiction, Plagiarism, Ethical and Legal Standards
Course-IV
PEDAGOGY OF MATHEMATICS
1.1 Meaning, Nature, and scope of mathematics.
1.2 History of Mathematics with special emphasis on teaching of mathematics.
1.3 Contributions of Indian Mathematicians a) Aryabhatta b) Brahmagupta c) Varahamihira d) Bhaskaracharya e) Srinivasa Ramanujan.
1.4 Contributions of Western Mathematicians a) Euclid b) Pythagoras c) Renedescarte d) Geroge Cantor.
1.5 Correlation of Mathematics with other school subjects and with other branches Of mathematics.
Unit-2: Aims and objectives of teaching Mathematics
2.1 Need for establishing general objectives for teaching mathematics.
2.2 Aims, Values and general objectives of teaching mathematics.
2.3 Specific objectives and teaching points of various content areas in different Branches of secondary school mathematics.
2.4 Recommendations of various Educational Committees and Commissions as Regards to Aims and Objectives of Teaching Mathematics.
2.5 Meaning and Concept of Academic Standards of CCE.
2.6 Linking Blooms Taxonomy with Academic Stands.
Unit-3: Methods, Approaches and Strategies in Teaching and Learning of Mathematical Concepts
3.1 Nature of Concepts, types of Concepts, Concept Formation and concept Assimilation; distinguishing and stating necessary and sufficient conditions in The process of teaching concepts. Comparing and contrasting. Giving counter Example and non example in teaching concepts. Planning and implementation Strategies in teaching concepts.
3.2 Creating awareness among student teachers on various concepts of Arithmetic, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry and Probability and Statistics from classics VI to X.
3.3 Methods of Teaching Mathematics: Inductive and Deductive: Analytic and Synthetic: Laboratory. Heuristic, Project Method and Activity Based Teaching.
3.4 Problem solving- Stages and Steps in problem solving; Discovering or Exploring various options for solving a given problem in Algebra, Arithmetic, Geometry, Trigonometry, Probability and Statistics.
3.5 Concept Attainment Model of Jerome Bruner.
Unit-4: Planning for Teaching – Learning Mathematics
4.1 Microteaching: Concept, Definition, Microteaching cycle, Components of Microteaching, Merits and Limitations.
4.2 Microteaching Skills: Introducing a lesson, Explaining a Concept, Stimulus Variation, Illustrating with Examples, Probing Questioning, Reinforcement, Structuring Classroom Questions, and Blackboard writing.
4.3 Planning of Instruction: Unit plan, Period plan based on Blooms Taxonomy and Academic standards.
4.4 Technology Integrated Lesson-Planning the Lesson by digital technology.
Unit-5: Learning Resources in Mathematics
5.1 Mathematics Text Book – Importance and Criteria of good Mathematics text Book.
5.2 A Critical Analysis of existing Secondary School Mathematics Text Books.
5.3 Audio, Visual and Multimedia resources – Selection and designing.
5.4 On line Resources – ICT based Pedagogical tools.
5.5 Using community resources for mathematics learning. Visits, mathematical Field trips and excursions.
5.6 Handling hurdles in utilizing resources.
Course-IV
PEDAGOGY OF SOCIAL SCIENCES
Unit-1: Social Sciences as an integrated area of Study
1.1 Meaning, Nature and Scope of Natural and Social Sciences
1.2 Distinction between Natural and Social Sciences
1.3 Meaning, History, Nature, Scope and Development of Social Studies
1.4 Distinction between social sciences and social studies
1.5 Understanding society through various social sciences
Unit-2: Aims Objectives and Academic Standards of Social Sciences
2.1 Major aims and objectives of teaching Social Sciences
2.2 Bloomıs taxonomy of Educational Objectives
2.3 Academic Standards and Learning outcomes of teaching Social Sciences
2.4 Recommendations of NPE 1986, NCF 2005, APSCF 2011
2.5 Values of Teaching Social Sciences
Unit-3: Approaches, Methods, Strategies and Techniques of Teaching Social Sciences
3.1 Meaning, need and significance of various approaches, methods, strategies and Techniques of Teaching Social Sciences
3.2 Teacher Centred Approaches – Lecture, Lecture-demonstration, Source and Supervisory Study 3.3 Learner centered approaches –Project, Problem Solving, Discussion, and Inductive And Deductive, Observation, Constructivistic Approach
3.4 Strategies / Techniques - Brain Storming, Team Teaching, Mind Mapping, Questioning
3.5 Activities – Dramatisation, Role play, Field Trips, Social Science Clubs, Exhibitions
Unit-4: Planning in Teaching Social Sciences
4.1 Microteaching – Meaning, Concept and Steps
4.2 Microteaching Skills - Introduction, Explanation, Questioning, Reinforcement, Stimulus Variation 4.3 Year Plan and Unit Plan
4.4 Need and Importance of Lesson Planning (Period Planning)
4.5 Technology Integrated Lesson Planning
Unit-5: Teaching Learning Resources in Social Sciences
5.1 Community Resources – Human and Material
5.2 Social Science Library, Laboratory and Museum
5.3 Need and Significance of Current and Controversial issues in teaching social Sciences
5.4 Handling hurdles in utilizing resources
5.5 Professional Development of Social Sciences Teacher
Course-IV
PEDAGOGY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Unit-1: Introduction to Science
1.1. Meaning and Functions of Science
1.2. Nature and Scope of Science
1.3. Structure of Science
1.4. Branches of Science
1.5 History of Biological Science
Unit-2: Aims and Values of Biological Science
2.1. Aims of Teaching Biological Science
2.2. Values of Teaching Biological Science
2.3. Competences of a Biological Science Teacher
2.4. Correlation of Biological Science with other school Subjects
Unit-3: Objectives of Teaching Biological Science
3.1. Meaning and Importance of objectives
3.2. Revised Blooms Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
3.3. Instructional Objectives and specifications with examples
3.4. Academics Standards mentioned in the school biological science text Book published by government of Andhra Pradesh
Unit-4: Methods and Techniques of Teaching Biological Science
4.1 Micro Teaching Techniques
4.2 Lecture Method, lecture Demonstration Method, and Laboratory Method
4.3 Scientific Method (Inductive and Deductive Method)
4.4 Project Method
Unit-5: Planning for Teaching Biological Science
5.1 Year Plan
5.2 Lesson Plan
5.3 Period Plan (Herbartian and Constructivist approach and CCE Model)
5.4 Learning Experiences
5.5 Planning ICT Applications in Learning Biology
Course-V
PEDAGOGY OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES
1.1 Science and Physical Sciences – Meaning, Nature, Scope and Importance
1.2 Structure of Science – Syntactic Structure (Process of Science – Domain of Inquiry), Substantive Structure - Product of Science-Facts, Concepts, Theories, Laws and Principles – characteristics in the context of Physical Sciences (citing examples)
1.3 Values of Learning Physical Sciences
1.4 Correlation of Physical Sciences with Mathematics, Biological Sciences, Social Studies, Languages, Fine Arts, Environment, Health, Development, Peace and Equity
1.5 Analysis of selected concepts of Physics and Chemistry from 6-10 classes
Unit-2: Development of Science - Physical Sciences
2.1 Milestones in the Development of Sciences – Physics and Chemistry
2.2 Contributions of Western and Indian Scientists
2.3 Landmarks, Status and Development Indian Science and Technology
2.4 Physical Science and Human Life
2.5 Rationale in Inspiring Students to study Physical Science
Unit-3: Aims. Objectives and competencies of teaching Physical Sciences
3.1 Aims and Objectives of Teaching Physical Sciences
3.2 Taxonomy of Educational Objectives – Bloom, Krathwohl, Simpson, et al – Revised Bloomıs Taxonomy and Higher Order Thinking Skills
3.3 Instructional Objectives of Teaching Physical Sciences
3.4 Behavioural or Specific Objectives of Teaching Physical Sciences
3.5 Competencies for Teaching of Physical Sciences
Unit-4: Approaches, Methods and Techniques of Teaching Physical Sciences
4.1 Concept of Teaching with special reference to Physical Science – Approaches and Methods – Student Participation in Learning
4.2 Teacher-centred Methods - Lecture, Lecture-cum-Demonstration, Historical
4.3 Student-centred Methods - Heuristic, Project, Scientific and Laboratory (Illustration of each method by taking examples from specific contents of Physics and Chemistry)
4.4 Modern Teaching Techniques - Brainstorming, Team Teaching and Models of Teaching – Concept Attainment Model and Enquiry Training Model
4.5 Microteaching - Concept and Meaning, Skills of Microteaching, Practice of Microteaching Skills
Unit-5: Planning for Teaching Physical Sciences
5.1 Importance of Planning for Teaching
5.2 Year Plan
5.3 Unit Plan
5.4 Period Plan (Lesson Plan) – Herbertian Steps vs. Constructivist Approach
5.5 Teaching Strategies and Academic Standards, CCE model period plan for Classroom teaching
Course-V
PEDAGOGY OF ENGLISH
Unit-1: Introduction to ELT
1.1 Meaning, nature and scope of ELT
1.2 Status of English Language in the global and Indian contexts
1.3 Aims and Objectives of Teaching English in India
1.4 Language and Education Policy in India
1.5 Teaching English in Bilingual/Multi-lingual contexts
Unit-2: Methods and Approaches in ELT
2.1 Method, Approach and Technique
2.2 Grammar Translation Method, Direct Method, Bilingual Method and Dr. Westıs Method
2.3 Oral, Situational and Structural Approaches
2.4 Communicative Language Teaching
2.5 Micro skills in ELT
Unit-3: Listening and Speaking Skills
3.1 Types and Sub-skills of Listening
3.2 Techniques of and materials for teaching Listening
3.3 Sub-skills of Speaking
3.4 Techniques of and materials for teaching Speaking
3.5 Activities to develop Listening and Speaking skills.
Unit-4: Reading and Writing Skills
4.1 Types and Sub-skills of Reading; Methods of Teaching Reading
4.2 Reading and Reflecting on text
4.3 Mechanics of Writing
4.4 Sub-skills and techniques of Writing
4.5 Activities to develop Reading and Writing skills.
Unit-5: Developing integrated skills and use of ICT in English Language Teaching
5.1 Teaching of Prose
5.2 Teaching of Poetry
5.3 Use of Multi-media in ELT
5.4 Online resources for ELT
5.5 ELT and Social Networking
We are Leading Institute providing Regular / Vedioes / Live Coaching under NVIE Trust . We Provides Coaching For Classes 1 to 12 (CBSE - CHSE - ICSE - HSC ). We also provide NEET - JEE -OUAT Entrance Preparation for +2 Science Student . We provide Bank - Railway - SSC - OTET - OSSTET - B.Ed Odisha - CT Odisha - Others Entrance Coaching for graduate .